Hallo yodabosten,
Ich nehme an, man muss Fp in zwei Teilkräfte teilen (Fpx und Fpy) ...
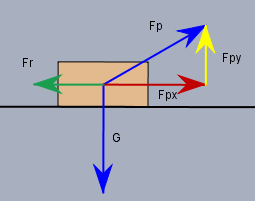
So ist es: $$F_{Px} = \frac 12 \sqrt 3 F_P \approx 34,64 \text N \\ F_{Py} = \frac 12 F_P = 20 \text N$$(Bem.: \(F\) ohne einen \(\vec {\phantom F}\) soll hier nur der Betrag der Kraft sein)
... und dann die Reibung berechnen
auch richtig. Die Kraft \(F_y\), die die Kiste auf den Boden ausübt, ist $$F_y = mg - F_{Py} = 10 \text{kg} \cdot g - \frac 12 F_P = 78,1 \text N$$und damit ist die Reibungskraft$$F_R = \mu_R \cdot F_y = 0,3 \cdot 78,1 \text N = 23,43 \text N$$und nach der berühmten Newton'schen Formel \(F = m \cdot a\) ist die Beschleunig \(a\) (in der Horizontalen)$$a = \frac{ F_{Px} - F_R }{m } \approx 1,12 \frac{\text m}{\text s^2}$$